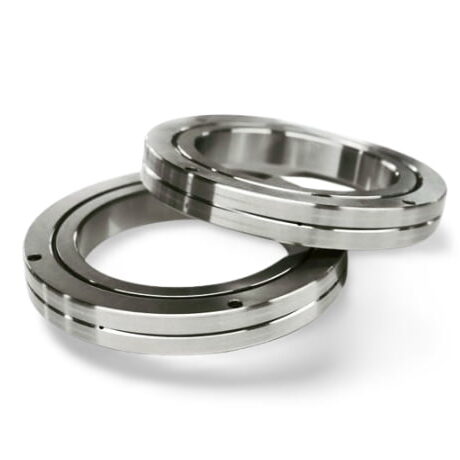
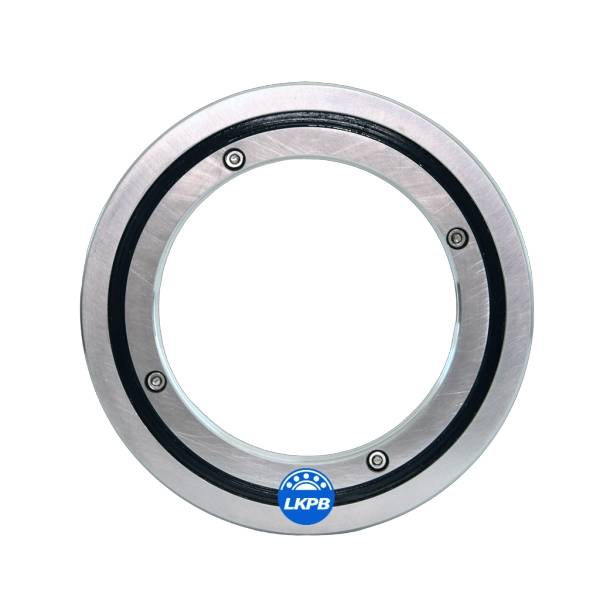
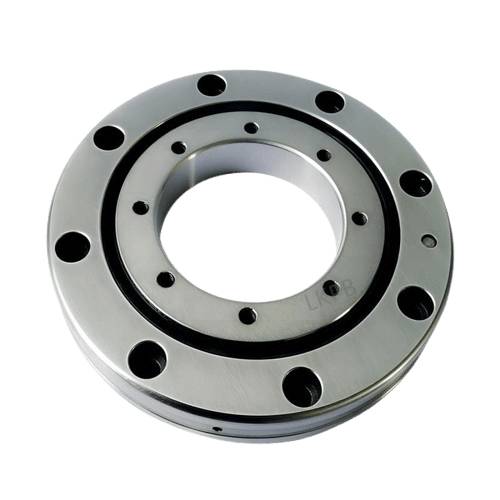
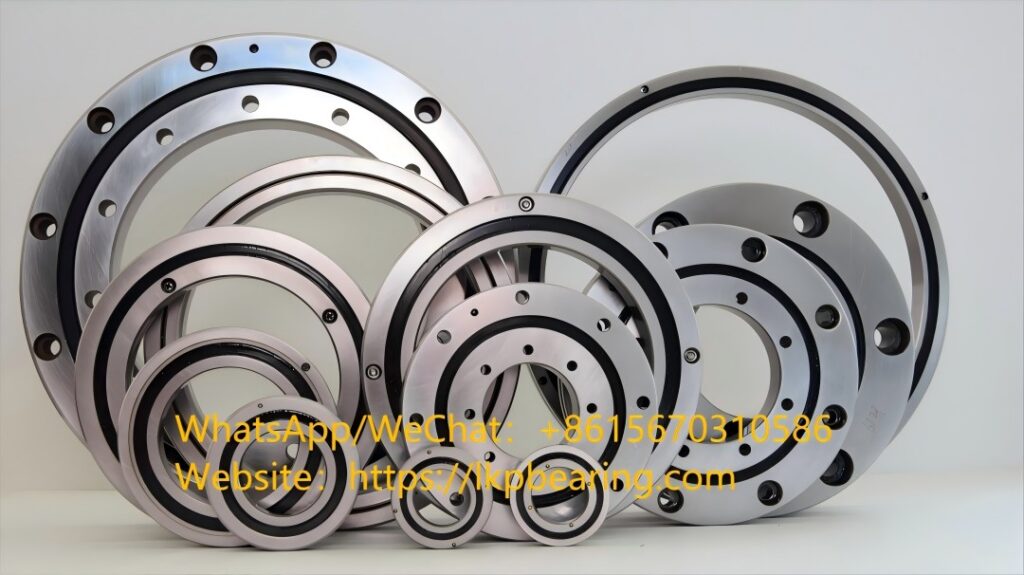
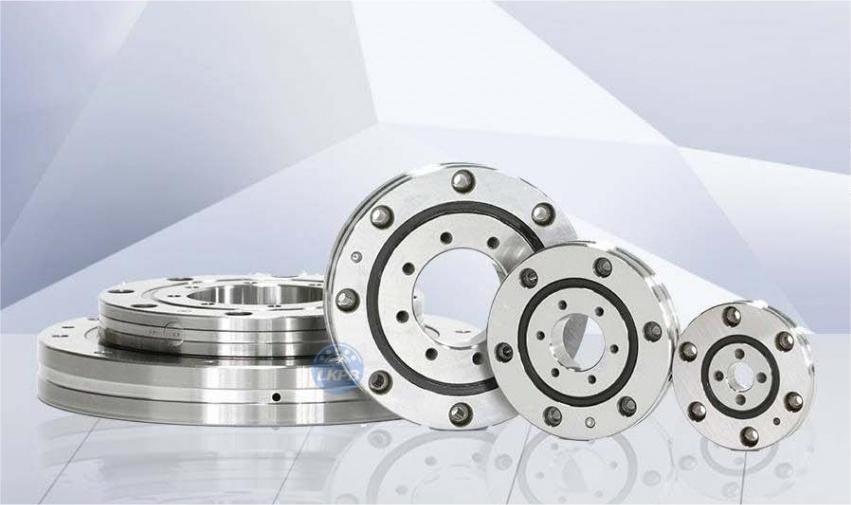
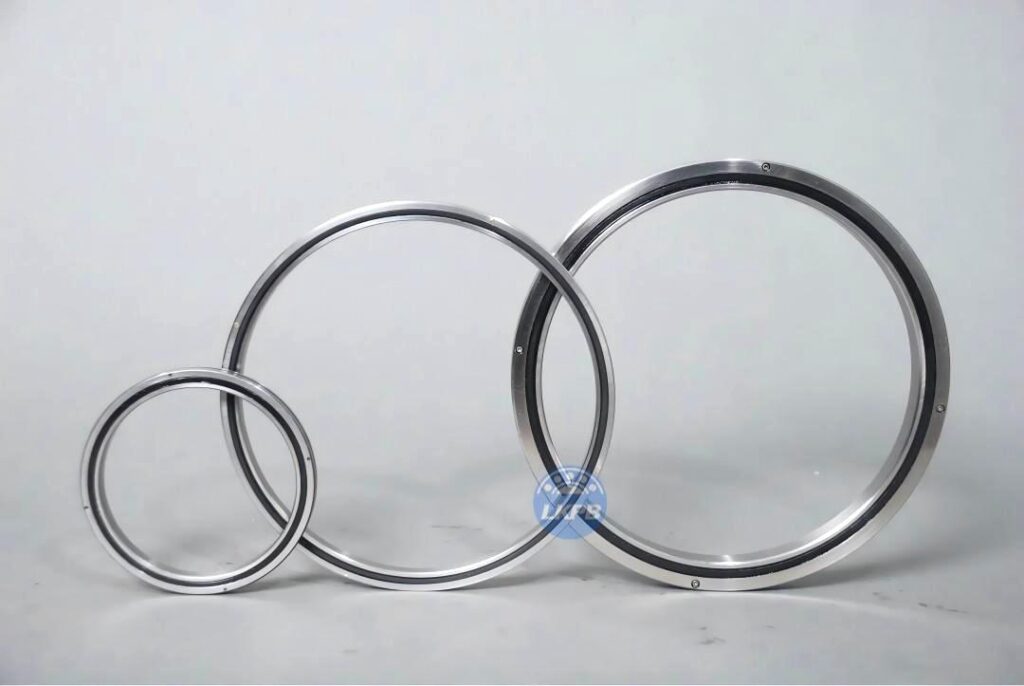
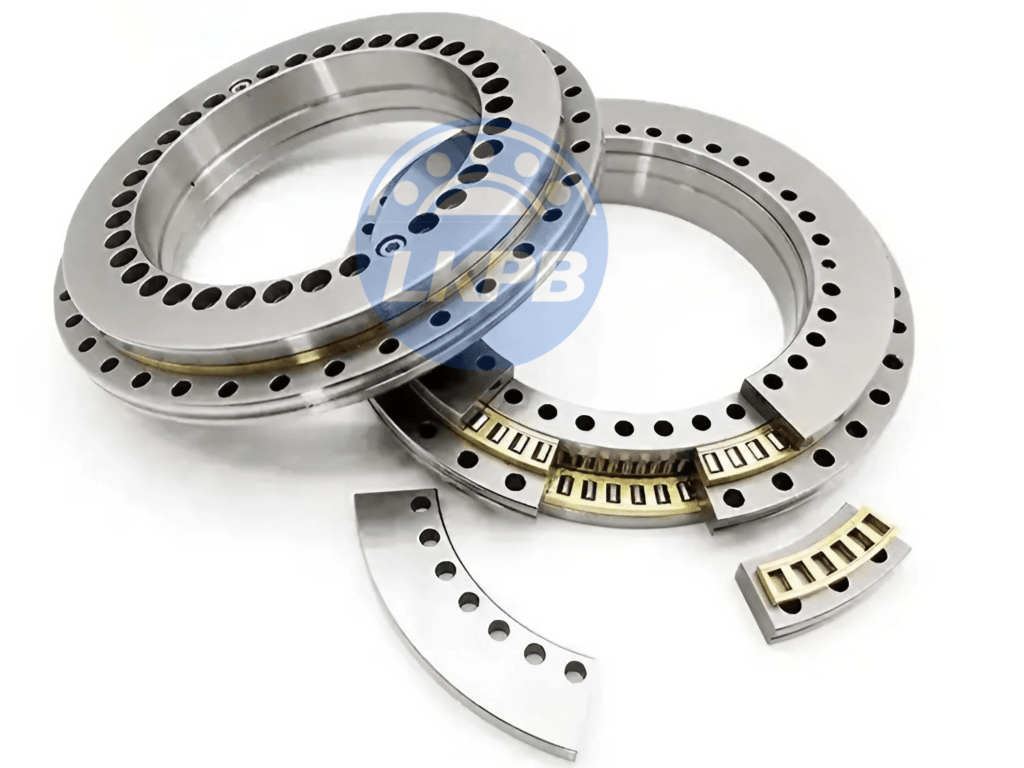
LKPB® strictly follows the ISO9001 quality system requirements for product quality control, relying on the professional technology of the bearing production base, the product quality is stable and cost-effective,
LKPB®, turning the world, carrying unlimited! We have served thousands of customers all over the world during the ten years of our establishment.
Our future goal is to become the most professional manufacturer of rotary table bearings and crossed roller bearings in China, and make LKPB® a world-class bearing brand.
This is our vision and direction!