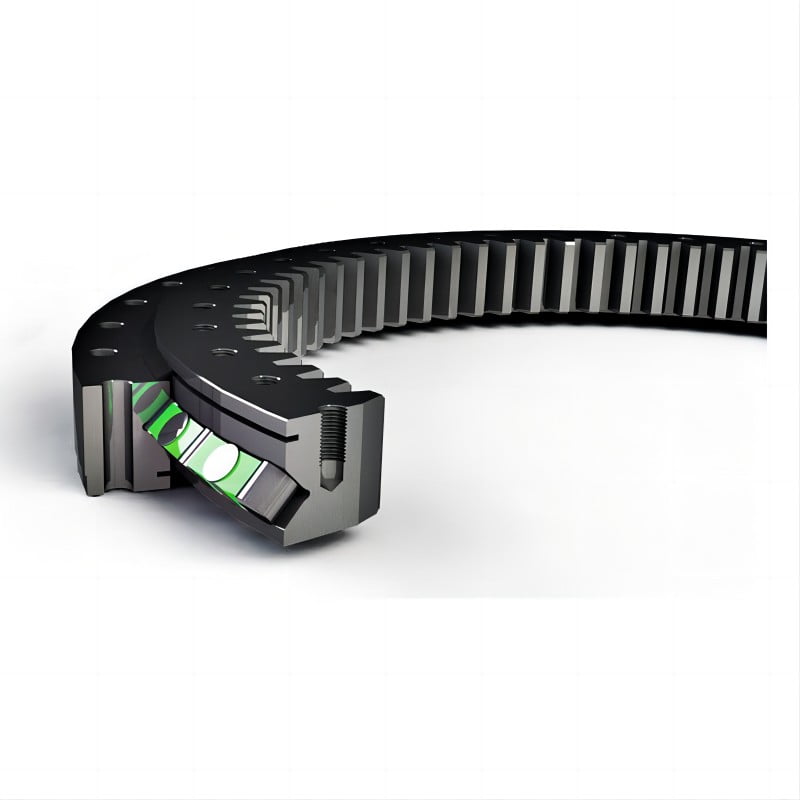
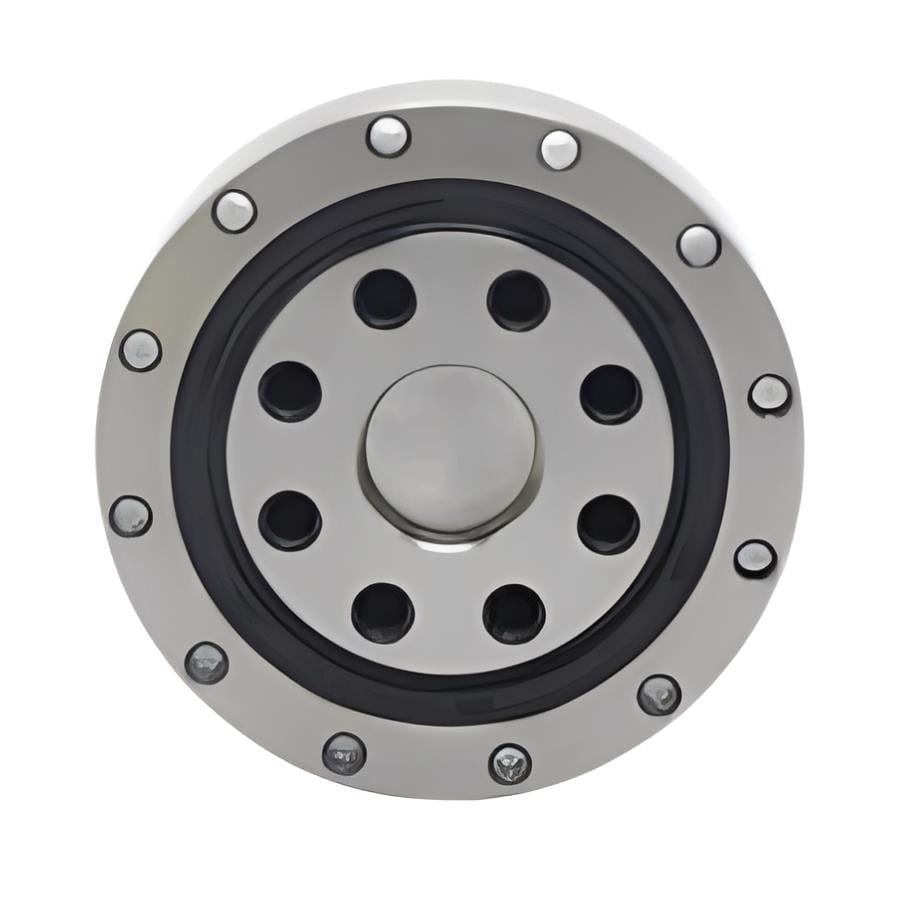
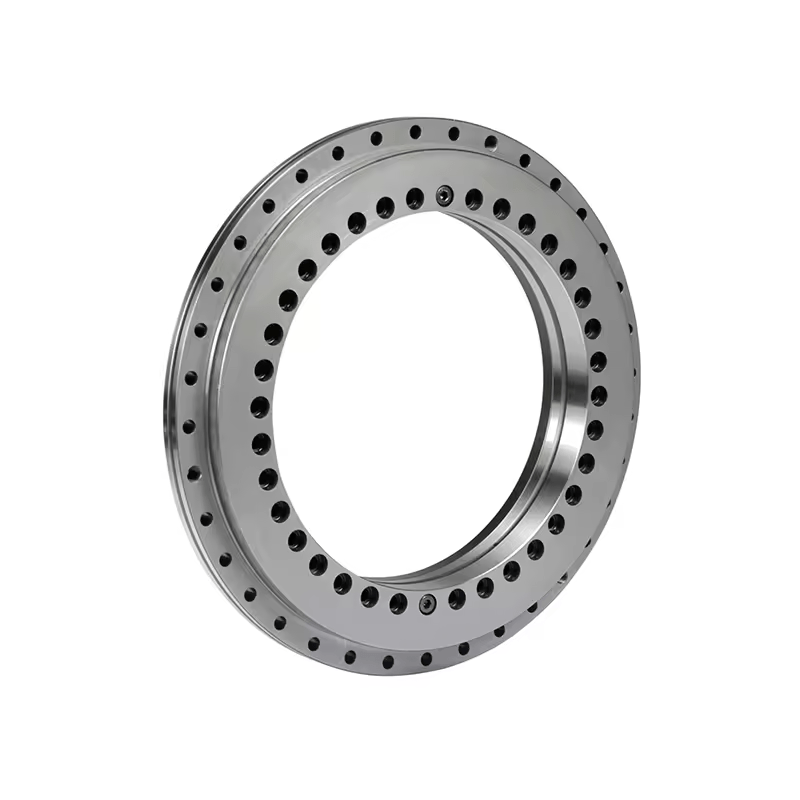
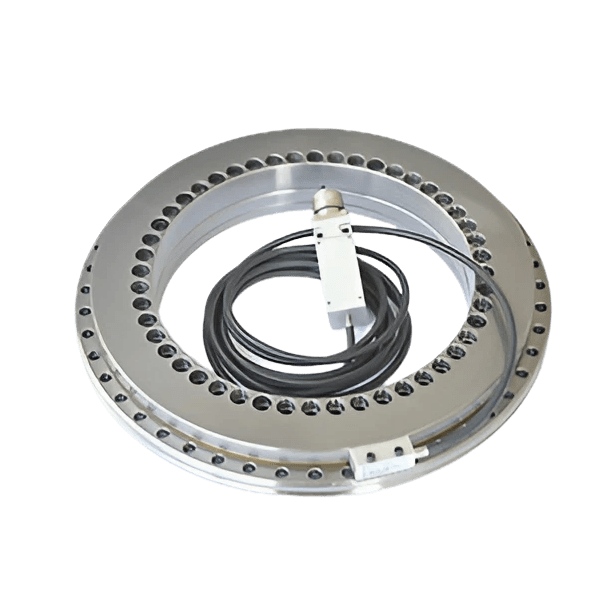
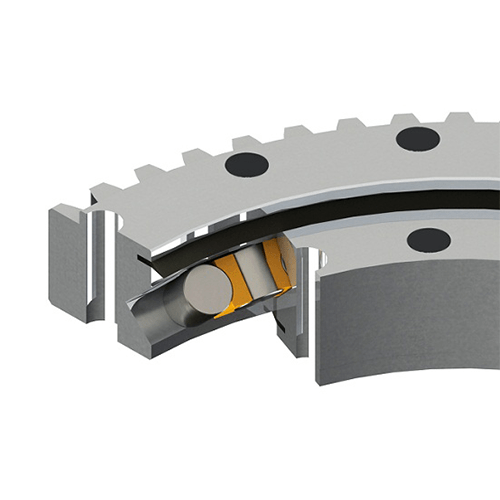
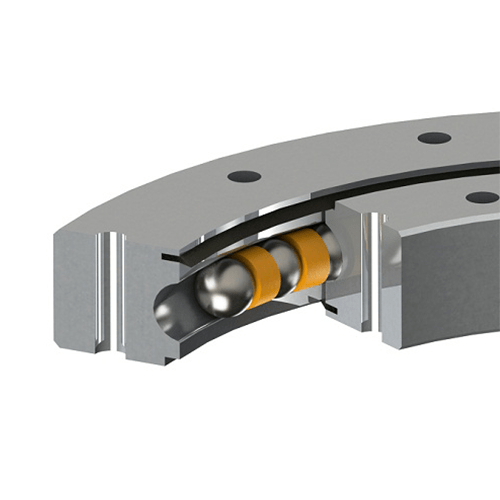
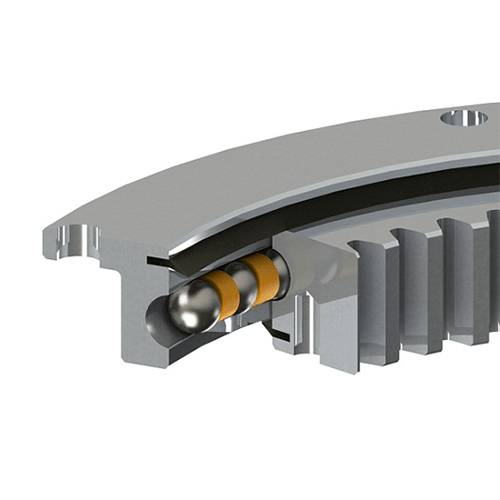
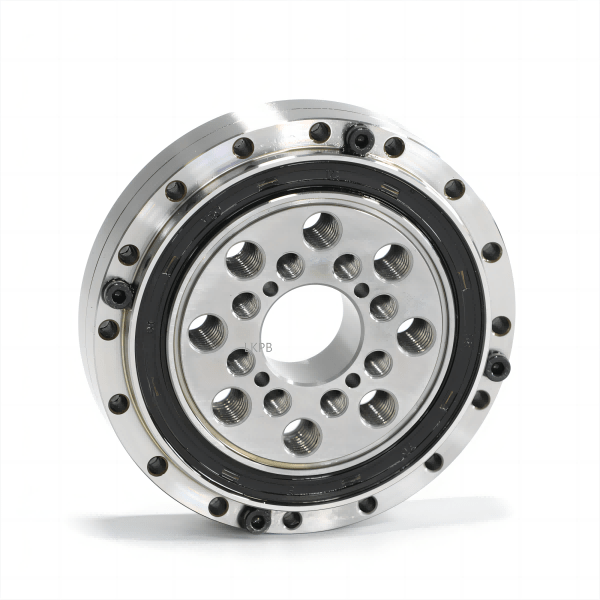
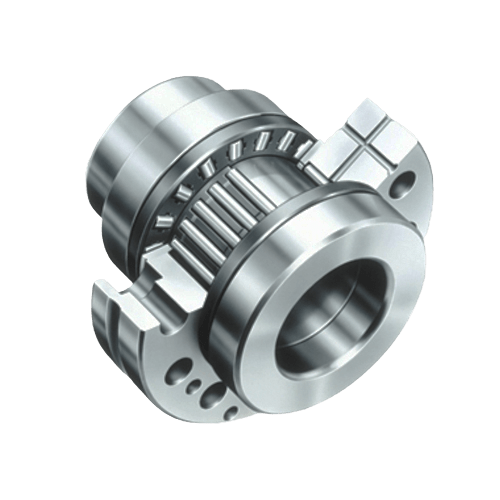
Bearings are mechanical components that support rotating shafts or axles and enable smooth rotational motion between two parts. They are used in a wide range of applications, including motors, wheels, gears, and various kinds of machinery. Bearings serve several important functions:
1. Reducing friction: Bearings minimize the friction between the rotating shaft and the stationary housing, allowing for smoother rotation and reduced energy loss.
2. Supporting loads: Bearings are designed to support radial loads (perpendicular to the shaft) and, in some cases, thrust loads (parallel to the shaft).
3. Positioning: Bearings help maintain the proper positioning and alignment of the rotating components.
4. Distributing loads: Bearings distribute the load evenly across their rolling elements (e.g., balls, rollers), preventing localized stress and wear.
There are several types of bearings, including:
1. Ball bearings: These use small spherical balls as the rolling elements and are suitable for high-speed applications.
2. Roller bearings: These use cylindrical rollers as the rolling elements and can handle heavier radial loads.
3. Thrust bearings: These bearings are designed to support thrust loads parallel to the shaft.
4. Sleeve bearings: These are simple bushings or plain bearings that rely on a lubricating film between the shaft and the bearing surface.
Bearings can be made from various materials, such as steel, ceramic, or plastic, depending on the application’s requirements for load capacity, durability, and operating conditions (e.g., temperature, lubrication).
Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of bearings are crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable operation of rotating machinery.
China has made significant strides in developing its precision bearing industry in recent years. Here are some key insights:
- Increased focus on R&D: Chinese bearing manufacturers have been investing heavily in research and development to improve the quality, precision, and performance of their bearings. This has allowed them to catch up with international standards and compete more effectively in the global market.
- Adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies: Chinese companies have been adopting advanced manufacturing technologies, such as computer numerical control (CNC) machining, precision grinding, and surface treatment processes, to enhance the accuracy and reliability of their precision bearings.
- Expansion of product range: While China initially focused on producing standard bearings, many Chinese companies have expanded their product range to include high-precision bearings for various applications, including aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery.
- Emphasis on quality control: To meet the stringent requirements of precision bearings, Chinese manufacturers have implemented robust quality control measures, such as clean-room environments, stringent inspection processes, and adherence to international quality standards like ISO 9001.
- Domestic market growth and international expansion: The growing demand for precision bearings in China’s domestic market, driven by industries like automotive, wind energy, and high-speed rail, has fueled the growth of the precision bearing industry. Additionally, Chinese bearing manufacturers have been actively pursuing international markets, leveraging their competitive pricing and improving quality.
- Collaboration and acquisitions: Some Chinese bearing companies have formed strategic partnerships or acquired foreign companies to gain access to advanced technologies, expertise, and established distribution networks.