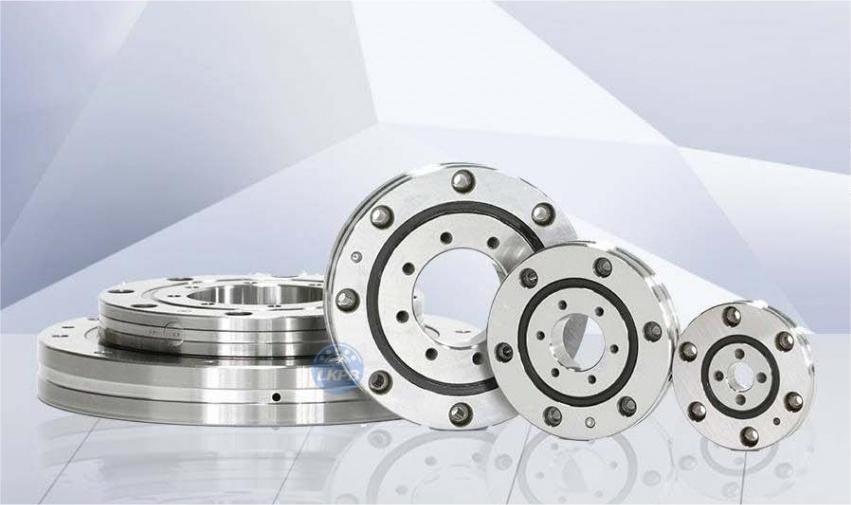
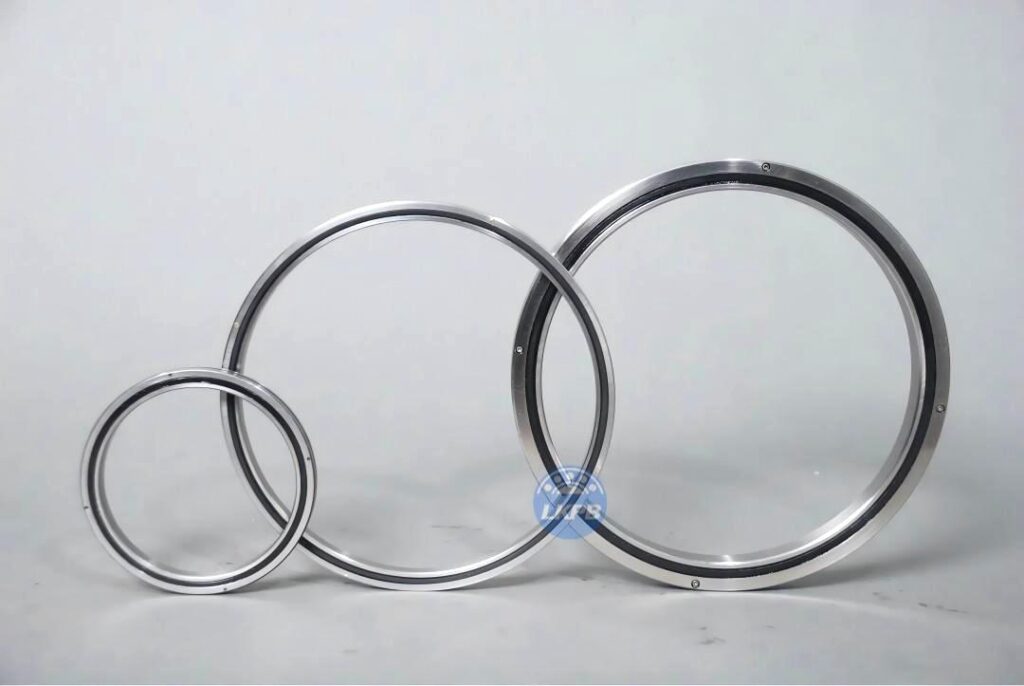
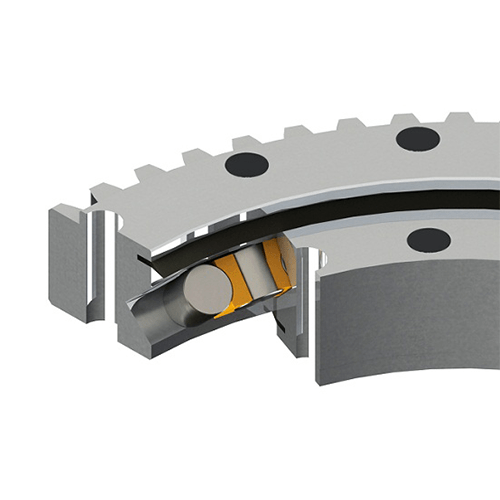
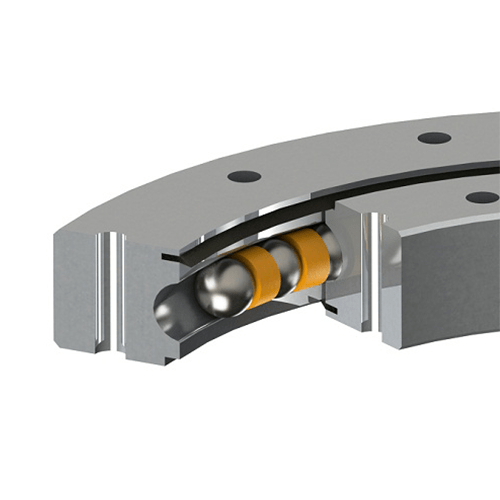
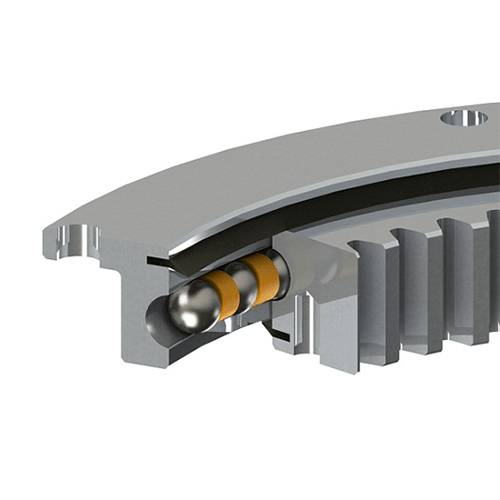
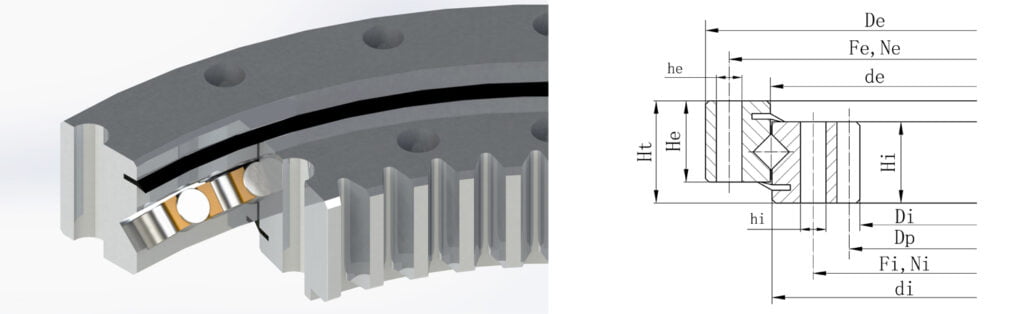
LKPB®
Get a free quote fast
Please let us know the product model and quantity you need and we will provide the most competitive quote! Alternatively, you can contact our knowledgeable customer service team:
Email: [email protected] WhatsApp/Wechat: +86 13613886217